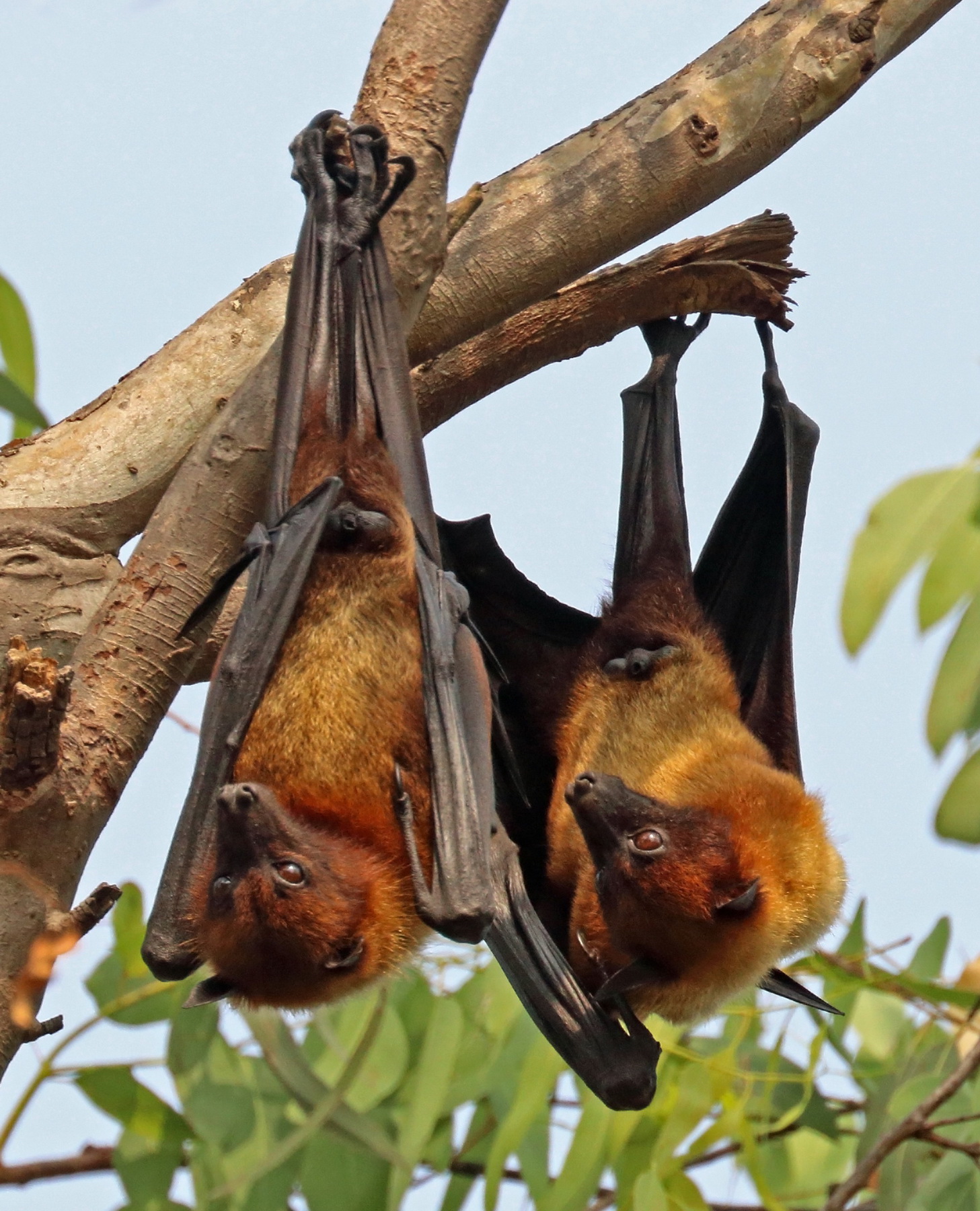
Indian Flying Fox

Also known as Chamadchidiya, whorwangoa, vadvagor
Lowest risk
Native
The Indian flying fox, also known as the greater Indian fruit bat, is a species of flying fox found in the Indian subcontinent. It is one of the largest bats in the world. It is of interest as a disease vector, as it is capable of transmitting several viruses to humans. It is nocturnal and feeds mainly on ripe fruits, such as mangoes and bananas, and nectar. This species is often regarded as vermin due to its destructive tendencies towards fruit farms, but the benefits of its pollination and seed propagation often outweigh the impacts of its fruit consumption.
- Range mass
- 600 to 1600 g
- Average length
- 23 cm
- Range wingspan
- 1.2 to 1.5 m
- Average basal metabolic rate
- 1.622 W
- Breeding interval
- Mating occurs once yearly.
- Breeding season
- Mating season is between the months of July and October.
- Range number of offspring
- 1 to 2
- Average number of offspring
- 1
- Average number of offspring
- 1
- Range gestation period
- 140 to 150 days
- Average weaning age
- 5 months
- Average age at sexual or reproductive maturity (female)
- 1.5 years
- Average age at sexual or reproductive maturity (female)
Sex: female - 365 days
- Average age at sexual or reproductive maturity (male)
- 1.5 years
- Average age at sexual or reproductive maturity (male)
Sex: male - 365 days
- Range lifespan
Status: captivity - 31 (high) years
- Average lifespan
Status: captivity - 31.4 years
Silbernagel, E. 2005. "Pteropus giganteus" (On-line), Animal Diversity Web. Accessed November 10, 2020 at https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Pteropus_giganteus/

If you notice an inaccuracy, have additional information to add, or want to suggest an edit contribute here